PCB vs PCBA The distinction between PCB vs PCBA is vital among individuals considering venturing into electronics manufacturing, product development, as well as circuit board design. Although these terms are interchangeably used, they can be classified to denote various phases in the process of manufacturing electronics. This in-depth answer will clear the air on the issue PCB vs PCBA and give you the knowledge to make the right choice on your electronics projects.
What is PCB: The Backbone of electronic

What is PCB?
Printed Circuit Board (PCB vs PCBA) is the bare base of any electronic gadget. It is the skeleton that offers structural reinforcements and serves as a connection of electrical devices to the electronic component. The PCB has a non-conductive substrate, usually fiberglass (FR4) with copper conductors etched into its surface. These offer the routes through which electric charges can pass thus communicating between the various destinations on the board.
The fabrication of PCB vs PCBA is a glaring venture. To start with, the board is designed on a special software which lays out the boards with the components placed and the electrical connections. The substrate would be treated then using multiple layers of copper foil which in turn is etched to form the required circuit patterns. Lastly, bare board will be completed by a protective solder mask and holes will be drilled to form component holes.
Important features of PCB vs PCBA
The PCBs are available in many variations as per applications. Single-layer PCB vs PCBA s have components and traces on one side and are suitable to more simple circuits. With the double layer PCBs both sides bear components and traces which are connected inside by plated holes referred to as vias. In multi-layer PCBs there are several internal layers, whereby multilayers permit circuit complexity and a large component density by utilizing the layers.
The substrate material plays a big role in the performance of PCB vs PCBA. The FR4 fiberglass is very strong mechanically and insulative against electricity. High frequencies require special materials such as Rogers or Teflon that have better electrical properties. A current-carrying capacity of the traces is determined depending on the copper thickness, which is commonly calculated in ounces per square foot.
Understanding PCBA: The Whole Solution

What is PCBA?
Printed Circuit Board Autonomy (PCBA) is the latest development in the PCB vs PCBA contradiction. It is basically PCB loaded with electronic parts via a number of assemblies. The PCBA is the working electronic circuit, which can do its job intended i.e. processing of signals, motor controlling or handling power distribution or whatever.
PCB to PCBA conversion has highly advanced manufacturing processes. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) placement employs very accurate machines to place very small parts in the most accurate way. The through-hole insertion of components needs special equipment in which bigger components are inserted through holes that are drilled. The whole assembly then undergoes reflow or wave soldering process to make a permanent electrical connection.
The Path of PCBA manufacturing Process
The precursor to PCBA production is detailed design audit and procurement of parts. The engineers ensure that the availability of all the components and their compatibility with the design of the PCB vs PCBA. Then, a pattern used to place solder balls is drawn using a stencil. The components are then automatically placed by pick-and place machines along the assembly drawings.
Soldering is done differently with regard to the components. Reflow soldering applies predetermined warming curve to soften up solder paste and provide surface-mount components with trustworthy connections. Wave soldering : Passing of the board through hot solder to join the through hole components. Lastly, the completed board will be subjected to a series of tests just to make sure that the board works normally as well as meet the required quality requirements.
What is the difference between PCB and PCBA?

Usability and utility
The first one in the PCB vs PCBA contrast is functionality. PCB is only the building block – it cannot do any electronic job alone. It would be such a house with the framework, but with no electric wiring, water or fixtures. A PCB vs PCBA on the other hand is the entire working electronic assembly that is ready to insert into the final product.
In manufacturing terms, PCBs need less manufacturing processes and quality screening. It lies in making sure that the trace geometry, electrical continuity and mechanical integrity are provided. The PCBA manufacturing process requires a higher level of complexity, such as board to component alignment, quality soldering, and tests of the full functionality of the PCB vs PCBA.
Considerations on cost and Time
Comparative analysis of the cost depicts great differences between the PCB and PCBA manufacturing. The cost of PCB vs PCBA manufacturing is based mostly on size, number of layers and material specification. Other components of PCB vs PCBA cost are the cost of components, labor used in assembly, testing needs, and possible yield losses.
The considerations about time-to-market are also very different. Depending on their level of difficulty and capabilities of suppliers, PCB vs PCBA fabrication mostly takes place between 1 and 3 weeks. Compared to PCB vs PCBA, the manufacturing process needs time to be spent on designing the procurement of components, assembly facility, and test processes, which can drag the schedule by a couple of weeks.
Manufacturing Supply Chain and Logistics
When PCB vs PCBA manufacturing is contrasted, the complexity side of manufacturing supply chains jumps up. The raw materials used in PCB manufacturing are substrates, copper foil, and chemicals and these are managed. The assembly of PCB vs PCBA not only has many individual components to be sourced but also has many suppliers with varying lead times and a range of availability issues.
The need of quality control also increases with PCBA production. Whereas PCB vs PCBA testing is mostly concerned with electrical continuity and mechanical characterization, PCB vs PCBA testing may involve functional characterization, environmental stress testing and verification against numerous industry standards.
Applications and Use Cases
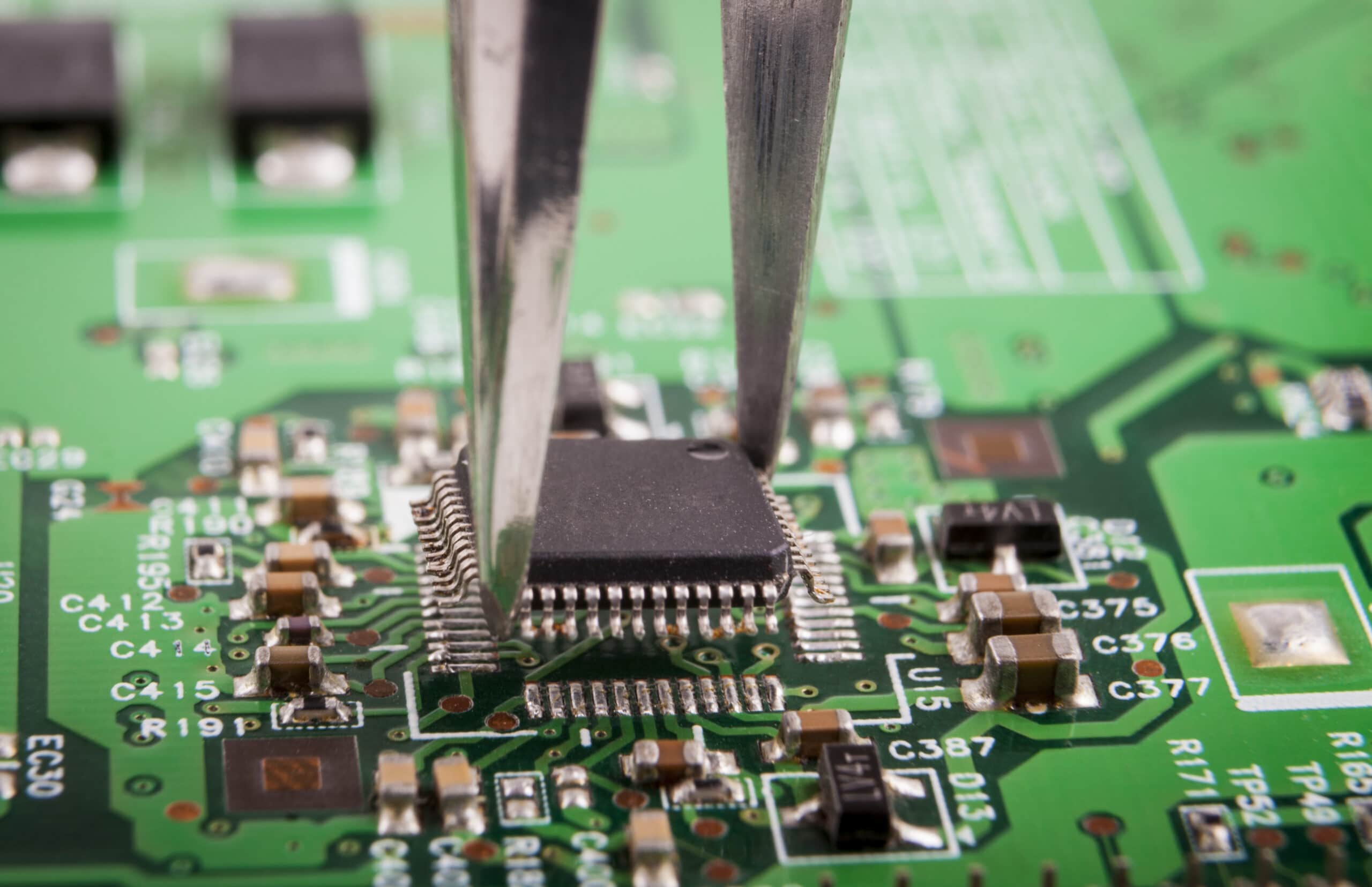
What are the circumstances when PCB is selected?
In a number of cases, it is reasonable to choose bare PCBs. Firms that have an in-house assembly capacity may decide to buy PCB vs PCBA s because they do not want to lose track of the assembly process. Prototyping and research Prototyping and experimental work PCBs are used in research and in educational institutions. Also, it can be advantageous to separate PCB and assemblies processes (where required in low-volume or highly specialized applications).
What to use PCBA?
The special strengths ofPCB vs PCB vs PCBA solutions are in the cases of high-volume production when the main focus is on manufacturing efficiency and cost optimization. Manufacturers that lack assembly facilities are able to utilize the expertise and investment on equipment by PCBA manufactures. PCBA services can be beneficial to the time-sensitive project as they can optimize manufacturing operations and the project timeline in general.
Test and quality standards

Test conditions and PCB Testing Techniques
PCB vs PCBA testing is aimed at the testing of the electric and mechanical characteristics of the bare board. Continuity checks used in electrical testing ensure that the trace connections are not made incorrectly and isolation testing that no unintended connections are made between circuits. The mechanical testing involves the assessment of the physical specifications of the board such as the dimensional dimensions as well as stability of the material.
Protocols of PCBA Testing
Testing PCBA is much more detailed, and it goes through various stages of testing. In-circuit testing is used to test that each component is on its place but that simple operation is working. Functional testing will make sure that the built board does what it is supposed to do in a regular manner. Environmental testing exposes the PCB vs PCBA to stress on temperature, humidity and vibration in order to verify reliability.
Trends and Innovation in the Future
The electronics sector keeps changing, an aspect that affects the PCB vs PCBA as well as PCBA technologies. The force of miniaturization can be seen in the production of high-density PCBs and fine geometries of designs and small-sized packages of components. New high-frequency and high-power applications become possible with the help of advanced materials and manufacturing procedures.
The approaches of automation and industry 4.0 are transforming the manufacturing of PCB vs PCBA. Smart factories apply real-time data analysis in order to improve their assembly operations and determine potential quality problems at an early stage. With such innovations, the decision making PCB vs PCBA is steadily decreasing as we see the manufacturing of PCB vs PCBA becoming more flexible and cost-efficient.
Conclusion
This is because the decider of PCB vs PCBA is based on your needs, limitations, and capabilities of doing it. Knowledge of such inherent disparities between the two choices will help you make more informed choices regarding your electronic projects. Your success in such strategy can be achieved with the use of bare PCB to reach the greatest level of flexibility or full PCB vs PCBA -solutions to achieve the most efficient manufacturing process, yet it is always a matter of choosing the right partner that has the experience and the power to satisfy your requirements.
The boundaries between PCB and PCB vs PCBA services will continue to dissolve along with technology, however, the general concepts described in this guide will be as helpful in making informed choices in your own electronic manufacturing life.
(FAQs) About PCB vs PCBA
Q1 What is the major distinction between PCB and PCBA?
Their primary distinction is that PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a bare board that has only copper traces but does not have any components on it whereas the PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) is the PCB with the electronic components soldered onto the PCB and it is a complete functional electronic circuit.
Q2 Is PCBA a more costly version of PCB?
Indeed, PCBA is much more costly than PCB since it comprises a price of electronic components, labor costs of assembly, testing, and other manufacture processes. The unit costs of the components alone may go up to 3-10 times of the naked PCB price.
Q3 What are the production time of PCB and PCBA?
The production process of PCB has an average of 3 weeks or less, depending on complexity and specification. It takes more time to buy parts and assemble them in PCBA manufacturing, which, on average, adds 2-4 weeks to a time frame of PCB fabrication.
Q4 Is it possible to mount parts on PCB by myself?
Yes, you can yourself assemble components on PCBs assuming that you have an equipment and skill. The latest surface-mount technology, however, needs special equipment such as pick-and-place machines and reflow ovens and consequently, professional services of PCBA would be more feasible to use when standard applications are involved.
Q5 What is the testing between PCB and PCBA?
PCB testing is on electrical continuity, isolation and mechanical of the bare board. PCBA testing is more extensive where it entails in-circuit testing, functional testing and environmental stress testing to ascertain that the assembled board works according the set criteria under different conditions.
For More Information Visit Bratish Magazine