predictive maintenance software In today’s hyper-connected and data-driven world, companies across industries are racing to optimize operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition. Among the most transformative advancements in industrial technology is predictive maintenance software — a game-changing solution that leverages data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to forecast equipment failures before they happen. This revolutionary approach allows organizations to shift from reactive and preventive maintenance strategies to predictive and proactive ones, ultimately boosting productivity, extending asset life, and maximizing return on investment.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance: From Reactive to Proactive
Traditional maintenance strategies fall into two main categories: reactive and preventive. Reactive maintenance involves fixing equipment after it breaks down, which often leads to costly downtime, unexpected failures, and inefficient use of resources. Preventive maintenance, on the other hand, involves scheduled servicing based on time intervals or usage cycles, regardless of the equipment’s actual condition. While preventive maintenance reduces the risk of breakdowns, it can still be inefficient and expensive, as components may be replaced unnecessarily or too early.
Predictive maintenance (PdM) changes this paradigm entirely. Instead of responding to failures or relying on fixed schedules, predictive maintenance uses real-time data, machine learning, and advanced analytics to predict when a component is likely to fail — allowing maintenance to be performed exactly when needed. This approach minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
The Core Technologies Behind Predictive Maintenance Software

Predictive maintenance software relies on a combination of cutting-edge technologies to deliver actionable insights. Together, these tools transform raw data into meaningful predictions about equipment health and performance.
Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors
At the heart of predictive maintenance is data — and IoT sensors are the primary source. These sensors continuously monitor parameters such as vibration, temperature, pressure, noise, humidity, and electrical current. By capturing real-time operational data, they enable predictive maintenance systems to detect subtle changes that may indicate wear, misalignment, or impending failure.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning algorithms are essential for processing vast amounts of sensor data and identifying patterns that signal potential failures. By learning from historical performance data, AI models can predict future outcomes with remarkable accuracy. Over time, these algorithms become even more reliable, continuously improving their predictive capabilities as they analyze more data.
Big Data Analytics
Predictive maintenance involves processing and analyzing enormous volumes of data from multiple sources, including sensors, historical records, and operational systems. Big data platforms allow predictive maintenance software to handle this complexity efficiently, correlating diverse data streams and delivering actionable insights.
Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, machine, or system. Predictive maintenance software can integrate digital twins to simulate real-world conditions, test scenarios, and forecast outcomes. This helps engineers and maintenance teams anticipate failures more accurately and plan interventions with greater precision.
Cloud Computing
Cloud-based predictive maintenance solutions enable seamless data storage, processing, and analysis without the need for costly on-premises infrastructure. Cloud platforms also support scalability, remote monitoring, and collaboration across multiple locations, making them ideal for global operations.
Key Features of Predictive Maintenance Software
Modern predictive maintenance software platforms come equipped with a range of features designed to optimize asset management, streamline workflows, and deliver predictive insights.
Real-Time Monitoring
Continuous monitoring ensures that equipment health is tracked around the clock. The software instantly detects anomalies, sending alerts and notifications to maintenance teams before issues escalate.
Predictive Analytics and Failure Forecasting
The core functionality of predictive maintenance software is its ability to forecast potential failures. Predictive analytics use historical and real-time data to estimate remaining useful life (RUL) and pinpoint the optimal time for maintenance interventions.
Automated Alerts and Notifications
When the software detects abnormal conditions or predicts a potential failure, it automatically notifies maintenance teams. These alerts can be customized based on severity, asset type, or operational impact, ensuring the right response at the right time.
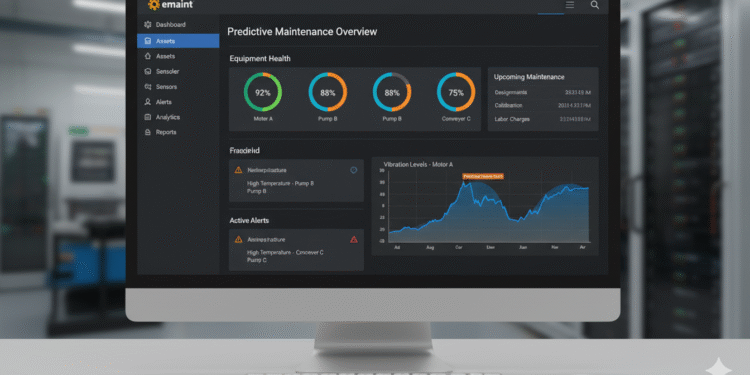
Asset Health Dashboards
User-friendly dashboards provide a comprehensive overview of equipment health, maintenance history, and predictive insights. Visualizations such as graphs, charts, and performance indicators make it easier to interpret data and make informed decisions.
Integration with CMMS and ERP Systems
Many predictive maintenance platforms integrate seamlessly with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. This integration automates work orders, streamlines inventory management, and aligns predictive insights with broader business operations.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance Software for Businesses
The adoption of predictive maintenance software delivers a wide range of benefits that extend far beyond simple cost savings. It represents a strategic investment in operational efficiency, asset longevity, and competitive advantage.
Reduced Downtime
Unplanned equipment failures can halt production lines, disrupt supply chains, and erode customer trust. Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime by identifying issues before they cause breakdowns, allowing maintenance to be scheduled during planned shutdowns.
Cost Savings
By performing maintenance only when necessary, companies avoid unnecessary repairs, reduce spare parts consumption, and optimize labor costs. Additionally, preventing catastrophic failures reduces the financial impact of major equipment damage.
Extended Asset Lifespan
Early detection of wear and potential failures helps prevent excessive stress on components, extending the overall lifespan of assets and delaying costly replacements.
Improved Safety and Compliance
Equipment failures can pose significant safety risks and lead to regulatory violations. Predictive maintenance reduces the likelihood of hazardous breakdowns, ensuring a safer workplace and helping organizations maintain compliance with industry standards.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Predictive maintenance improves asset reliability, reduces downtime, and optimizes maintenance schedules. This leads to smoother operations, higher productivity, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Data-Driven Decision Making
Predictive maintenance software provides detailed insights into asset performance and maintenance trends. These data-driven insights empower organizations to make smarter decisions about capital investments, resource allocation, and operational strategy.
Use Cases Across Industries
Predictive maintenance software is transforming a wide range of industries, each with its own unique challenges and opportunities. Its versatility and adaptability make it a valuable tool in virtually any sector that relies on machinery, equipment, or infrastructure.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, unplanned downtime can cost millions of dollars per hour. Predictive maintenance ensures continuous production by identifying potential failures in machinery such as motors, conveyor belts, and robotics. This leads to higher productivity, improved product quality, and reduced operational costs.
Energy and Utilities
Power plants, wind farms, and oil refineries operate complex and expensive equipment that must run reliably. Predictive maintenance helps utility companies detect wear in turbines, transformers, and pipelines before they fail, improving grid stability and minimizing energy disruptions.
Transportation and Logistics
From railway systems and aircraft fleets to delivery vehicles, predictive maintenance enhances reliability and safety across transportation networks. It helps detect issues such as engine degradation, brake wear, or wheel misalignment, preventing accidents and service delays.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, equipment failures can result in severe environmental damage and financial losses. Predictive maintenance enables operators to monitor drilling equipment, pumps, and pipelines in real time, preventing costly failures and ensuring operational safety.
Healthcare
Hospitals rely on critical equipment such as MRI machines, ventilators, and surgical tools. Predictive maintenance ensures these devices operate reliably, reducing downtime and safeguarding patient care.
Facilities Management
Building systems like HVAC, elevators, and lighting benefit from predictive maintenance by reducing energy consumption, extending equipment life, and improving occupant comfort.
Implementation Strategies for Predictive Maintenance Software
Successfully implementing predictive maintenance software requires more than just installing technology. It involves strategic planning, cultural change, and a focus on data-driven processes.
Define Clear Objectives
Start by identifying the specific goals of predictive maintenance — whether it’s reducing downtime, cutting maintenance costs, extending asset life, or improving safety. Clear objectives help shape the implementation strategy and measure success.
Assess Data Readiness
Predictive maintenance relies heavily on data quality and availability. Ensure that IoT sensors, data collection processes, and storage systems are in place and capable of capturing accurate, real-time information.
Choose the Right Software Platform
Select a predictive maintenance solution that aligns with your business needs, industry requirements, and existing infrastructure. Consider factors such as scalability, ease of integration, user interface, and vendor support.
Start with Pilot Projects
Launching predictive maintenance on a smaller scale allows organizations to validate the technology, refine workflows, and build confidence before full-scale deployment. Successful pilot projects also help secure stakeholder buy-in.
Train and Upskill Teams
Maintenance personnel, engineers, and operators must be trained to understand predictive analytics, interpret data, and act on predictive insights. Investing in workforce development is critical to maximizing the value of predictive maintenance software.
Monitor and Optimize
Predictive maintenance is not a one-time project but an ongoing process. Continuously monitor system performance, refine algorithms, and incorporate feedback to improve accuracy and outcomes over time.
Future Trends in Predictive Maintenance
As technology continues to evolve, predictive maintenance is poised to become even more intelligent, accurate, and impactful. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of this field.
Edge Computing
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data close to the source rather than relying solely on the cloud. This enables faster decision-making and real-time responses, which are critical in time-sensitive industrial environments.
AI-Powered Self-Healing Systems
Future predictive maintenance systems may go beyond predicting failures — they could automatically trigger corrective actions or self-adjust to prevent breakdowns without human intervention.
Advanced Digital Twins
Digital twin technology will become more sophisticated, integrating with AI and simulation tools to deliver highly accurate predictions, optimize asset performance, and support scenario planning.
Predictive Maintenance as a Service (PMaaS)
As-a-service models are gaining popularity, enabling organizations to access advanced predictive maintenance capabilities without significant upfront investment. PMaaS solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and regular updates.
Integration with Industry 5.0
The next industrial revolution will emphasize collaboration between humans and intelligent machines. Predictive maintenance will play a crucial role in this transformation by providing the data and insights needed for seamless human-machine interaction.
Conclusion: The Competitive Edge of Predictive Maintenance Software
Predictive maintenance software is more than a technological upgrade — it is a strategic imperative for businesses that want to stay competitive in a rapidly changing industrial landscape. By harnessing the power of data, IoT, AI, and analytics, predictive maintenance enables organizations to anticipate problems before they occur, optimize asset performance, and make smarter, more informed decisions.
As industries continue to evolve toward greater automation and connectivity, predictive maintenance will be at the heart of operational excellence. Companies that embrace this technology will not only reduce costs and extend asset lifespans but also unlock new levels of reliability, safety, and efficiency. In a world where downtime is no longer an option, predictive maintenance software is the key to ensuring that operations never miss a beat.