In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity for business has evolved from a luxury to an absolute necessity. With cyber threats increasing by 38% annually and the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.45 million, organizations of all sizes must prioritize robust security measures. This comprehensive guide will walk you through building an impenetrable cybersecurity framework that protects your business assets, customer data, and reputation.
Understanding the Current Threat Landscape
Modern businesses face an unprecedented array of cyber threats that can cripple operations within minutes. Ransomware attacks have surged 41% year-over-year, while phishing attempts now account for 36% of all data breaches. Small and medium enterprises are particularly vulnerable, with 43% of cyberattacks targeting businesses with fewer than 1,000 employees.
The financial implications extend beyond immediate losses. Recovery costs, regulatory fines, legal fees, and reputation damage can devastate companies for years. Organizations without proper cybersecurity for business protocols face average downtime of 287 days following a successful attack, making prevention far more cost-effective than recovery.
Essential Components of Business Cybersecurity
Network Security Infrastructure
Your network serves as the primary entry point for cybercriminals. Implementing multi-layered network security involves deploying advanced firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation. Zero-trust architecture should be adopted, where every user and device is verified before accessing network resources, regardless of their location or previous authentication status.
Next-generation firewalls with deep packet inspection capabilities can identify and block sophisticated threats that traditional security measures might miss. Network monitoring tools provide real-time visibility into traffic patterns, enabling rapid detection of anomalous behavior that could indicate a breach attempt.
Endpoint Protection and Device Management
Every device connecting to your business network represents a potential vulnerability. Comprehensive endpoint protection requires deploying enterprise-grade antivirus solutions, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and mobile device management (MDM) systems. These solutions should provide real-time threat detection, automated response capabilities, and centralized management across all devices.
Regular security updates and patch management are crucial components of endpoint security. Automated patch management systems ensure critical security updates are deployed promptly across all devices, reducing the window of vulnerability that cybercriminals often exploit.
Developing a Comprehensive Security Strategy
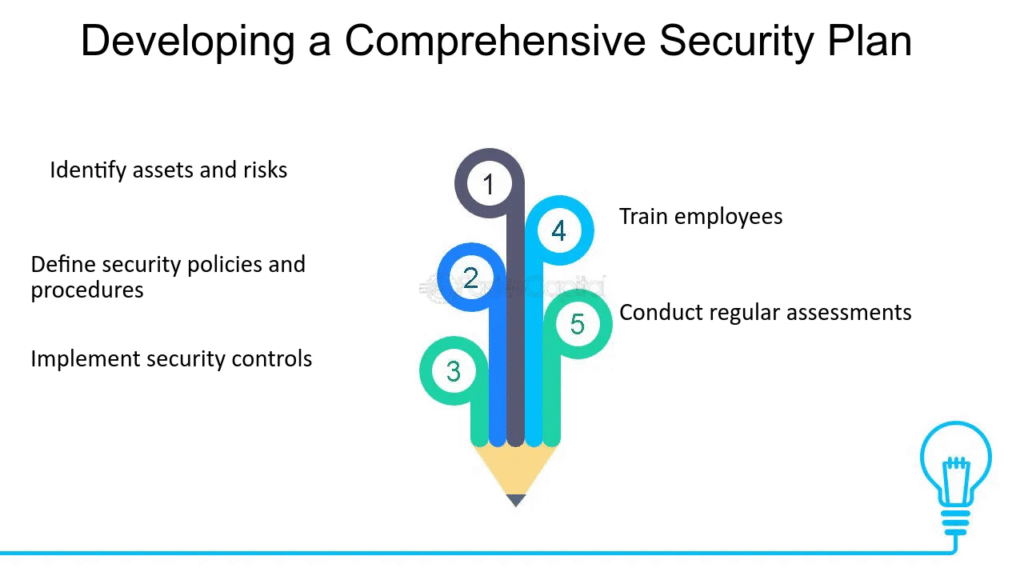
Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Management
Effective cybersecurity for business begins with thorough risk assessment. Organizations must identify all digital assets, evaluate potential threats, and prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. This process should include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits conducted by qualified professionals.
Regular vulnerability assessments help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats. Automated vulnerability scanners can continuously monitor systems for new weaknesses, while manual testing provides deeper insights into complex security gaps that automated tools might miss.
Access Control and Identity Management
Implementing robust access control mechanisms prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive business data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory for all users, while role-based access control ensures employees only access information necessary for their job functions.
Identity and access management (IAM) systems provide centralized control over user permissions, making it easier to grant, modify, or revoke access as needed. Regular access reviews ensure that former employees or contractors cannot access business systems, while privileged access management (PAM) solutions protect high-value administrative accounts.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Human error remains the leading cause of security breaches, making employee education a critical component of business cybersecurity. Comprehensive training programs should cover phishing recognition, password hygiene, social engineering tactics, and incident reporting procedures.
Regular security awareness training keeps cybersecurity top-of-mind for employees. Simulated phishing exercises help identify vulnerable users while providing targeted training opportunities. Creating a security-conscious culture where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities can significantly reduce successful attack rates.
Data Protection and Backup Strategies

Encryption and Data Classification
Protecting sensitive business data requires implementing encryption both at rest and in transit. All customer information, financial records, and proprietary data should be encrypted using industry-standard protocols. Data classification systems help organizations identify which information requires the highest levels of protection.
Database encryption, file-level encryption, and secure communication channels ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unusable to unauthorized parties. Regular encryption key management and rotation further enhance data security.
Backup and Recovery Planning
Comprehensive backup strategies are essential for business continuity. Organizations should implement the 3-2-1 backup rule: three copies of critical data, stored on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite. Cloud-based backup solutions provide scalable, secure storage options that can be accessed from anywhere.
Regular backup testing ensures that recovery procedures work effectively when needed. Recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) should be clearly defined and tested regularly to minimize business disruption during incidents.
Incident Response and Recovery

Developing an Incident Response Plan
A well-structured incident response plan enables organizations to respond quickly and effectively to security breaches. The plan should include clear roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and step-by-step procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Regular tabletop exercises and simulated incident response scenarios help teams practice their response procedures and identify areas for improvement. Having pre-established relationships with cybersecurity experts, legal counsel, and forensic investigators can expedite response efforts during actual incidents.
Business Continuity Planning
Cybersecurity incidents can disrupt business operations for extended periods. Business continuity planning ensures that critical functions can continue even during security incidents. This includes identifying essential business processes, establishing alternative work arrangements, and maintaining communication with customers and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Building strong cybersecurity for business requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technology, processes, and people. Organizations must stay vigilant, continuously update their security measures, and foster a culture of security awareness. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, businesses can significantly reduce their cyber risk and protect their valuable assets from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Remember, cybersecurity is not a one-time investment but an ongoing commitment. Regular assessments, updates, and improvements ensure that your security posture remains effective against evolving threats. Start building your comprehensive cybersecurity strategy today to safeguard your business’s future.
(FAQs) About Cybersecurity for Business
Q1 What is the most critical first step in implementing cybersecurity for business?
The most critical first step is conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify all digital assets, potential vulnerabilities, and threats specific to your business. This assessment provides the foundation for developing a targeted security strategy that addresses your organization’s unique risks and compliance requirements.
Q2 How much should a small business budget for cybersecurity?
Small businesses should allocate 3-5% of their annual revenue to cybersecurity initiatives. This typically ranges from $1,000 to $5,000 per employee annually, depending on the industry and risk profile. However, the cost of prevention is significantly lower than the average $4.45 million cost of a data breach.
Q3 What are the most common cybersecurity mistakes businesses make?
The most common mistakes include using weak passwords, failing to update software regularly, lacking employee training, not backing up data properly, and assuming they’re “too small to be targeted.” Many businesses also underestimate the importance of having an incident response plan and regular security assessments.
Q4 How often should businesses update their cybersecurity measures?
Cybersecurity measures should be reviewed and updated continuously. Critical security patches should be applied immediately, software updates monthly, employee training quarterly, and comprehensive security assessments annually. Threat landscapes evolve rapidly, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation.
Q5 What should a business do immediately after discovering a cyber attack?
Immediately isolate affected systems to prevent further damage, document the incident, notify relevant stakeholders including IT security teams, and begin following your incident response plan. Contact cybersecurity professionals and legal counsel as needed, and preserve evidence for potential forensic investigation. Avoid paying ransoms without expert consultation.
For More Information Visit Bratish Magazine